
Fifty-four species of bird are confined to the Sudan–Guinea savanna biome of Africa which extends across 22 countries. A network of 105 Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas (IBAs) has been identified which hold all 54 species, in only some 7% of the biome’s total area.
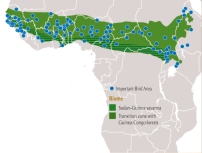
The Sudan–Guinea savanna biome extends across 22 countries from Senegal to Eritrea, and lies between the arid Sahel to the north and the Guinea–Congo rainforests to the south. Covering some 4.3 million km2, this vast area includes a wide variety of tropical woodland and wooded grassland habitats. Some 54 species of bird, such as White-crested Turaco Tauraco leucolophus, Blue-bellied Roller Coracius cyanogaster and Piapiac Ptilostomus afer, are largely or wholly confined to this biome, for which a network of 105 Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas (IBAs) has been identified. Between them, these sites hold all 54 species of this biome, as well as many other bird species and much other biodiversity. However, the IBAs cover only 283,000 km2 or c.7% of the biome’s total area, a further illustration of how the IBA approach provides a practical conservation focus on priority sites.
Related Species
References
Fishpool, L. D. C. and Evans, M. I. eds (2001) Important Bird Areas in Africa and associated islands: priority sites for conservation. Newbury and Cambridge, UK: Pisces Publications and BirdLife International.
Compiled: 2004
Recommended Citation:
BirdLife International (2004)
Important Bird Areas in biomes: an example from north-central Africa.
Downloaded from https://datazone.birdlife.org/sowb/casestudy/important-bird-areas-in-biomes:-an-example-from-north-central-africa on 22/12/2024