
A network of 34 Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas (IBAs) has been identified for Blue Swallow Hirundo atrocaerulea (Vulnerable) in Africa, covering an area of 20,612 km². The total estimated range or Extent of Occurrence (EOO) for this species is 246,000 km2; the IBA network therefore covers 8.4% of the EOO.
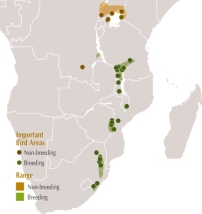
Blue Swallow Hirundo atrocaerulea (Vulnerable) migrates within Africa. It is globally threatened because of degradation and destruction of its grassland habitat in both its breeding and non-breeding ranges. The entire population of H. atrocaerulea (estimated at no more than 3,000 birds) nests in montane grasslands, covering small parts of seven countries of southern and eastern Africa. The species’s known non-breeding range centres on the moist tropical grasslands of the Lake Victoria basin (BirdLife International 2004). A network of 34 Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas (IBAs) has been identified for this species (see figure), 27 for breeding populations and seven in the less well-known non-breeding range(Fishpool and Evans 2001). Together, these sites cover a combined area of 20,612 km². The total estimated range or Extent of Occurrence (EOO) for this species is 246,000 km2. The IBA network therefore covers 8.4 % of the EOO.
Similar calculations (from data held in BirdLife’s World Bird Database) for the rest of the c.180 globally threatened, resident landbirds in Africa show that the IBAs selected for them cover a mean of 8.6 % of their EOOs. This demonstrates how the IBA approach focuses on the priority sites, where conservation efforts need to be targeted.
Related Species
References
Compiled: 2004
Recommended Citation:
BirdLife International (2004)
Important Bird Areas for globally threatened species: Blue Swallow.
Downloaded from https://datazone.birdlife.org/sowb/casestudy/important-bird-areas-for-globally-threatened-species:-blue-swallow on 22/12/2024